Incoterms, which stands for “International Commercial Terms”, is a standardised three-letter code set most commonly used in international transactions. These rules were created by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) to facilitate communication and understanding between buyers and sellers involved in international trade. Incoterms define the responsibilities, risks and costs associated with the transport and delivery of goods.
What is Incoterms?
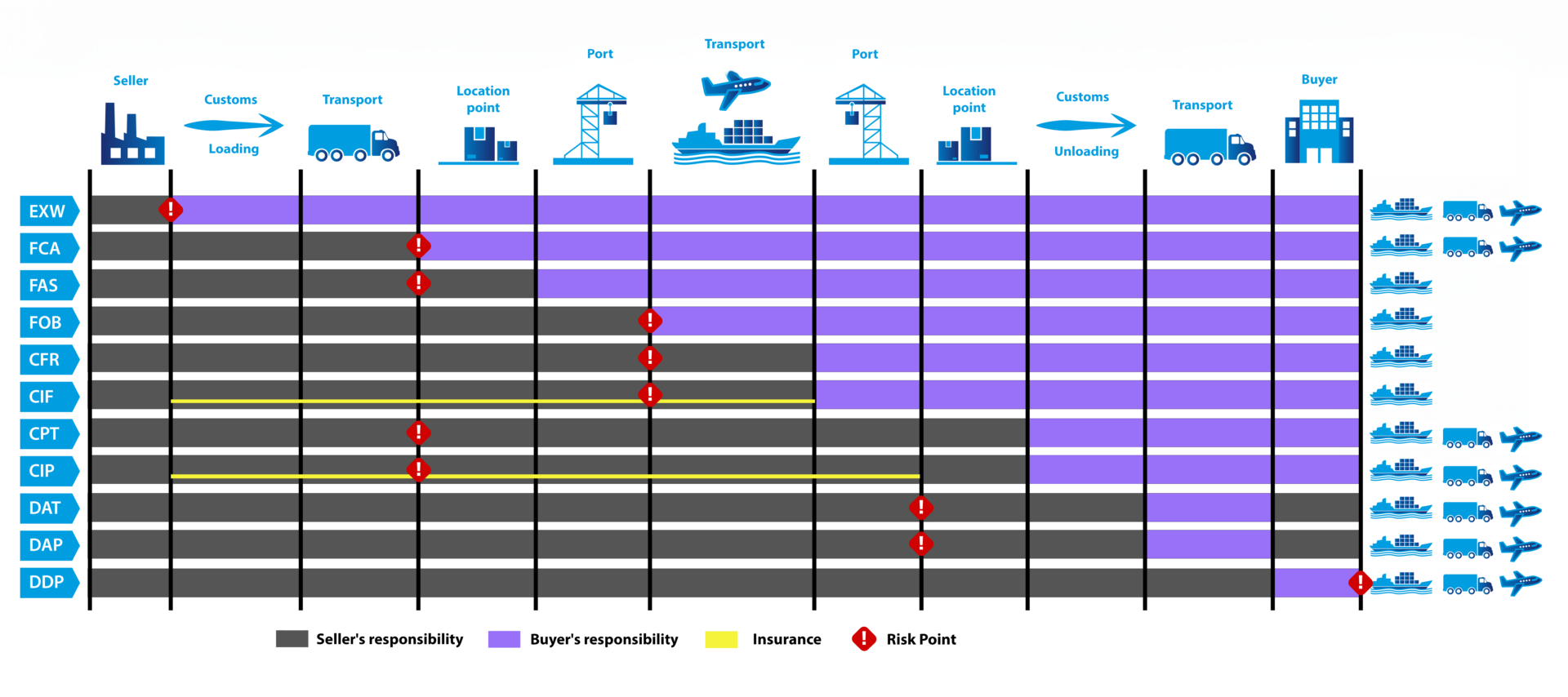
EXW (Ex Works): The seller provides the goods at their location. The buyer is responsible for all transportation costs, risks, and necessary customs clearance.
FCA (Free Carrier): The seller delivers the goods at the chosen delivery point, such as a warehouse or a carrier’s vehicle. At this point, the risks and responsibility for transportation transfer to the buyer.
FAS (Free Alongside Ship): The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the shore-based port, alongside the ship. The buyer assumes risks and responsibility when the goods are placed alongside the ship’s deck or at another specified location on the shore.
FOB (Free On Board): The seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the designated cargo port. When the goods are on the ship, the risks and responsibility transfer to the buyer.
CFR (Cost and Freight): The seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the specified port, covering transportation costs and providing cargo insurance. The buyer assumes responsibility and risk when the goods are loaded onto the ship at the port.
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the ship’s coastal port, covering transportation and insurance costs. The risk transfers to the buyer when the goods are on the ship.
CPT (Carriage Paid To): The seller covers the transportation costs of the goods to the specified destination. When the goods are handed over to the carrier, the risk transfers to the buyer.
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Specifies the terms of the trade contract regarding the delivery of goods between the seller and the buyer. CIP stipulates that the seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the specified destination, covering transportation costs, and providing cargo insurance.
DAT (Delivered at Terminal): Specifies the terms of the trade contract regarding the delivery of goods between the seller and the buyer. DAT establishes that the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the designated terminal at the destination, which can be a port terminal or another chosen location.
DAP (Delivered at Place): The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the named place, ready for unloading by the buyer. The buyer is responsible for unloading and customs duties.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the named destination, covering all costs, including customs duties. The buyer only needs to unload the goods.

